Microservices are a popular architecture that addresses the limitation and drawbacks of a legacy application.
Overview:
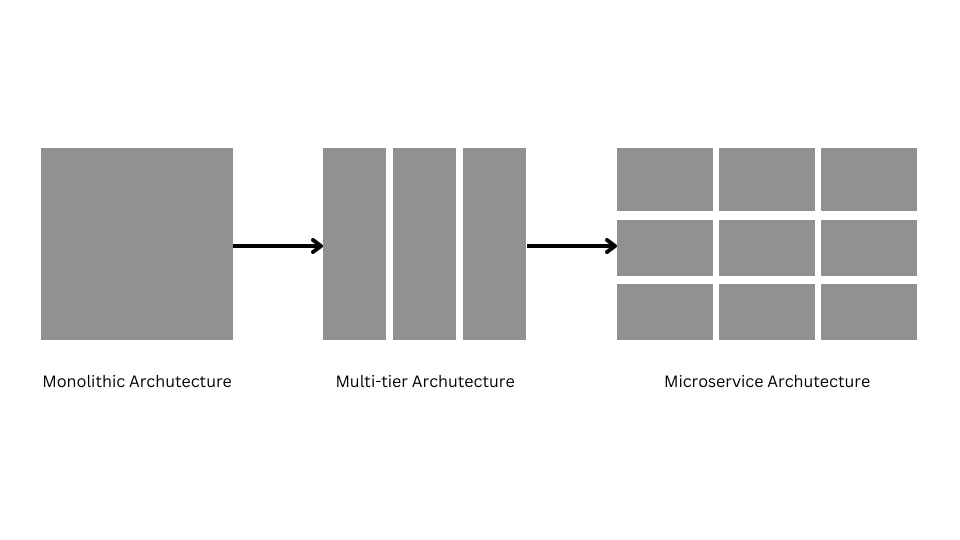
To understand the foundation of microservices, we need to take a look at the history and evolution of application design from various architectures:
Monolithic Architecture
Multi-tier Architecture
MicroServices Architecture
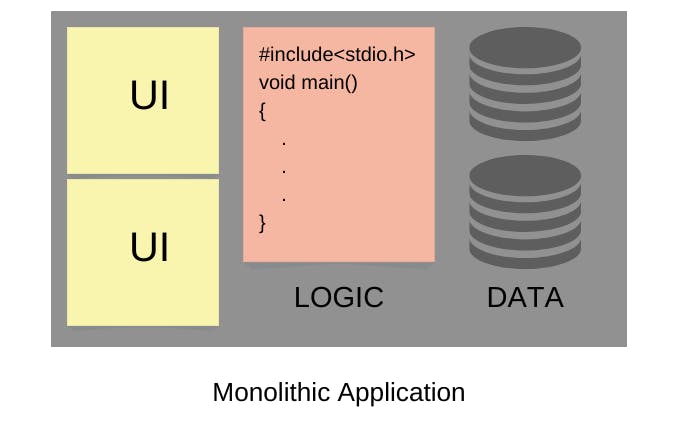
A straightforward way to build a simple application is to design it as a single piece of code encapsulating data storage and access, business logic and processes, & user interface.
That used to be the way applications and systems are designed and built in the early days.
Soon however this all-in-one code model showed its limits when building complex intricate systems.
Since everything is tangled together it becomes quickly difficult to maintain, evolve and scale such applications.
Improvements
Software Engineers propose the solution to this complex problem i.e Multi-tier Architecture.
Multi-tier Architecture where application components are separated into layers based on technical functions.
A common model is a 3-tier Architecture.
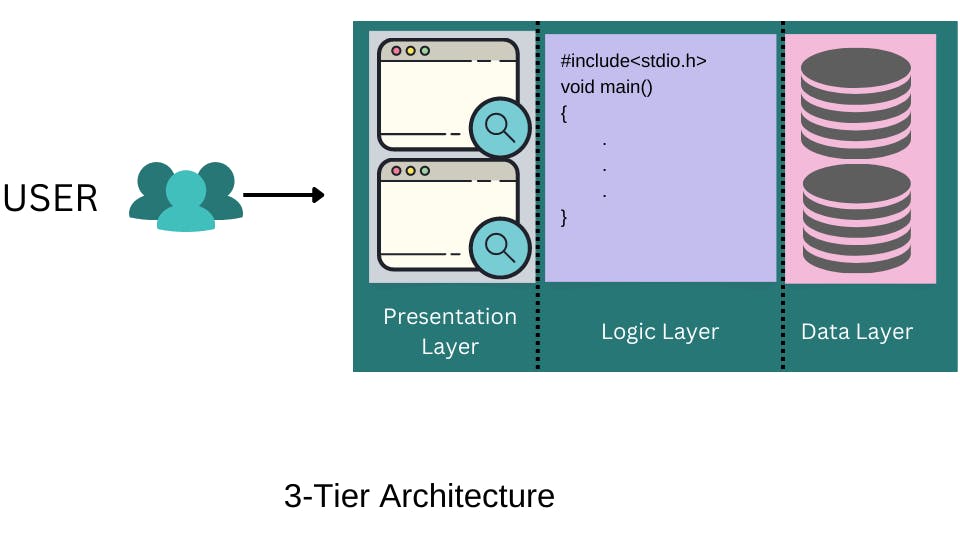
It consists of three logical layers:
Presentation Layer:
- It Covers all code and components responsible for the interaction with users through visual interfaces.
Logical Layer:
- It encompasses all the business logic and processes relative to the business functions, and
Data Layer:
- It deals with storing, accessing, and retrieving data when needed.
While separating logic and data into two different layers made things better, it was still a centralized way to design applications, and it didn't address quite well the challenges associated with complex applications and systems.
About Microservices
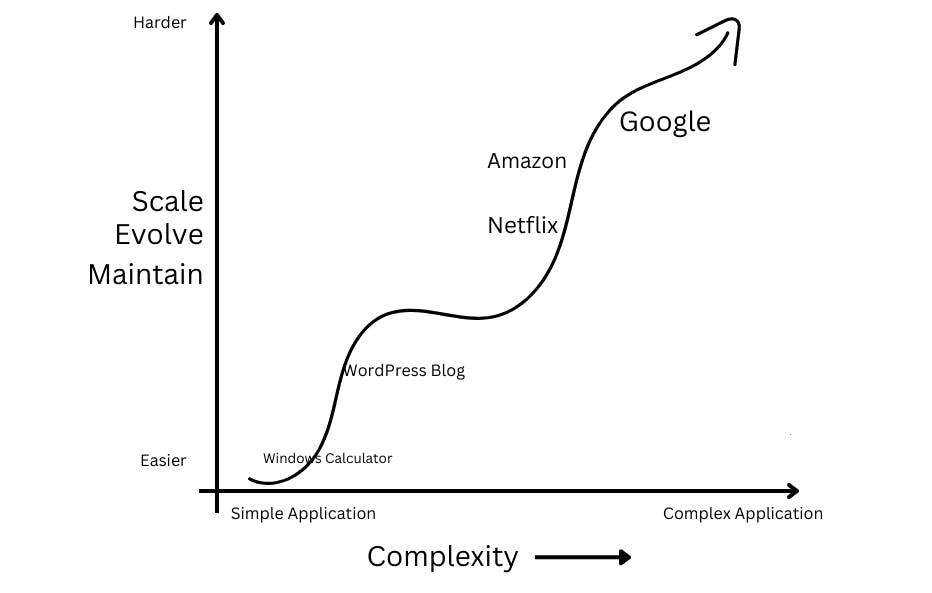
Application Complexity has been exponentially growing with the advent of the global high-growth web and mobile applications.
Maintaining, evolving, and scaling very complex applications like Amazon's E-commerce website, or Google search engine requires a design shift.
Here again, the best way to tackle complexity is by decomposing it into manageable chunks that is why software engineers decided to break apart the logic and data layers into smaller pieces called MicroServices.
Every microservice deals with one business function i.e end-to-end independency from other microservices.
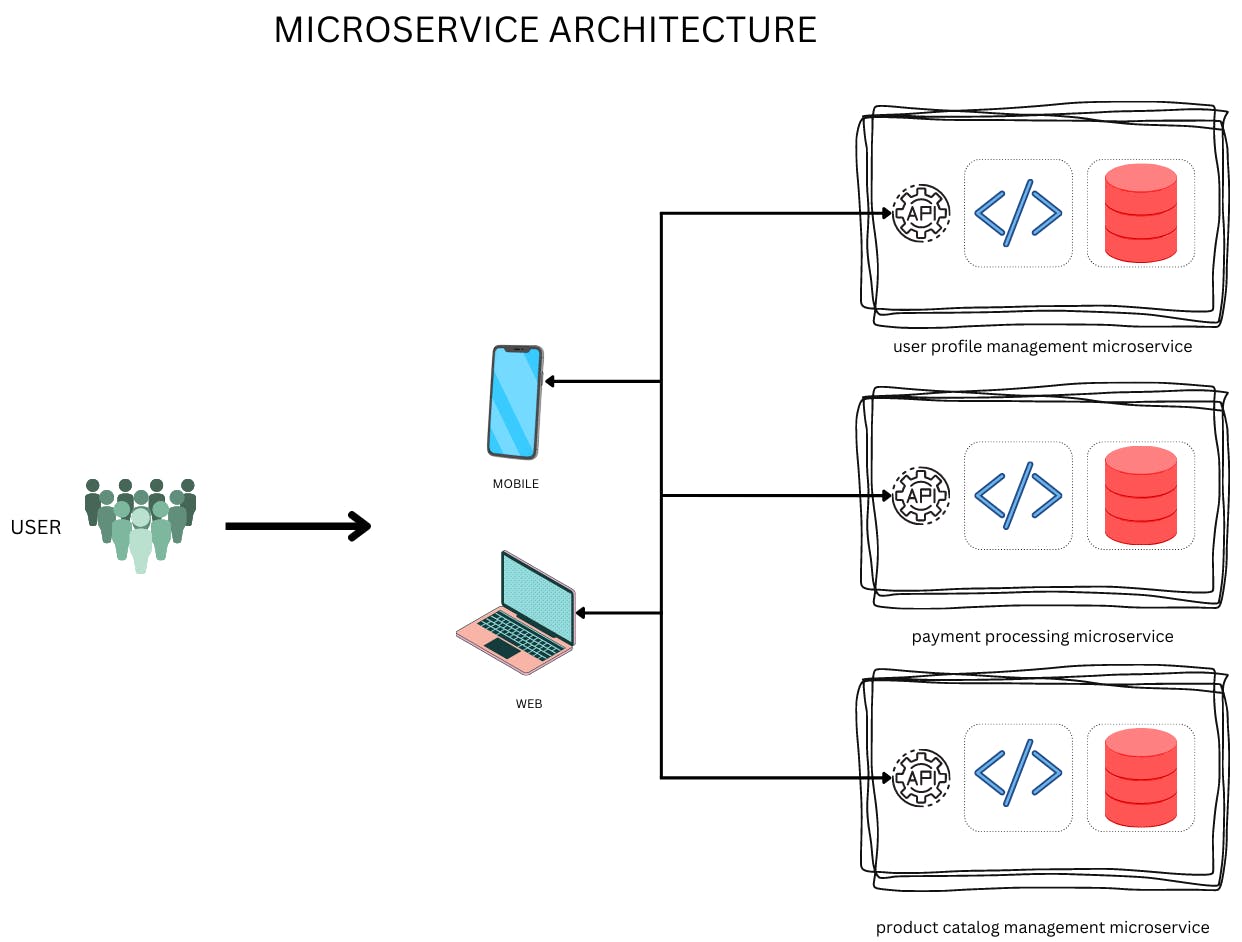
Microservices present simple easy to understandable APIs and communicate with each other using lightweight common protocols such as HTTP or message queues.
When an application is architected as a microservice, different teams can work separately and independently on different microservices, building new functions and evolving the business capabilities without impacting other teams and business functions.
Theoretically different teams could even use different programming languages and deploy their microservices to different infrastructure providers like AWS, GCP & Azure.
However for cost reduction and efficiency improvement and operational optimization reasons most organizations limit team choices to a set of approved tools, infrastructure providers, and programming languages.
Disadvantages / Problems with microservices
As Applications continue evolving and growing the number of microservices inside an organization could expand to tens hundreds or even thousands as this happens complexity starts creeping up again.
For example: If a microservice instance fails in production, it could generate a cascade of outages within other microservices. Since the architecture is highly distributed it could become difficult to identify the root cause and fix it in a timely manner.
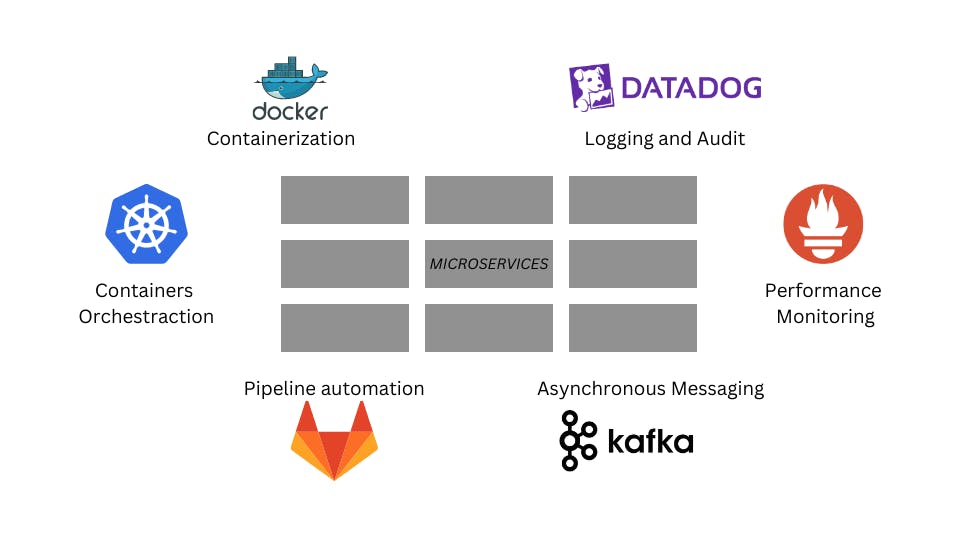
The Software engineering community has been creating and inventing new tools to tackle and contain the ever-growing complexity of highly distributed microservice-based systems.
Some of the most popular tools include containerization like docker, Container orchestration systems like Kubernetes (K8s), Pipeline automation like Jenkins, GitLab, GitHub Action, Asynchronous messaging like Kafka, Application performance monitoring tools like Prometheus, Logging & Audit tools like DataDog.
Monolithic Vs Distributed Application
Monolithic Application:
- Harder to maintain, Scale & Evolve.
Distributed Application:
- Harder to manage, monitor & Secure.